Because hydrogels have mechanical properties similar to those of natural biological tissue, freeze-drying technology is used to preserve their original active substances and physical structure, addressing storage issues, instability, and inconvenient handling.
A freeze-dryer freezes the hydrogel into a solid state at low temperatures. Then, under a certain vacuum environment, the water sublimates directly from the solid state to a gaseous state, removing the moisture and preserving the hydrogel. This low-temperature, vacuum-based process protects heat-sensitive substances, minimizes the loss of volatile components, and virtually eliminates microbial growth and enzyme activity, preserving the hydrogel's original properties to the greatest extent possible.
The application of freeze-drying technology in hydrogel materials is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
(1) Improving the physical properties of hydrogels: Freeze-drying technology can be used to prepare GelMA composite hydrogels, which can effectively improve the mechanical properties of GelMA, adjust the microstructure, such as swelling and porosity, and improve biocompatibility. It can meet the mechanical performance requirements of different tissues and organs and lay the foundation for the introduction of bioactive cells and the application of different living materials.
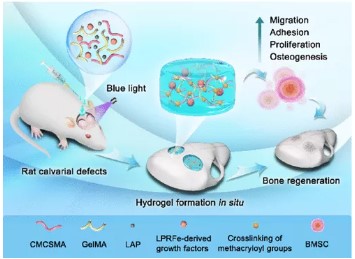
Schematic diagram of freeze-dried platelet-rich fibrin exudate loaded with carboxymethyl chitosan/GelMA hydrogel for effective bone defect repair.
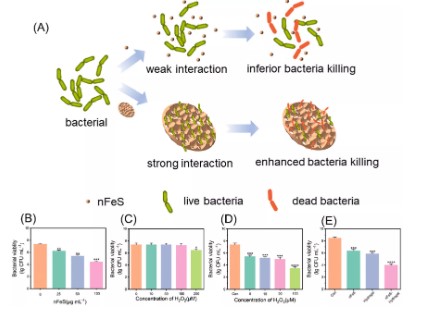
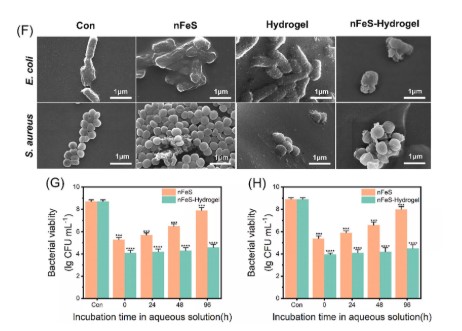
Schematic diagram of rapid bacterial capture and killing by freeze-dried nFeS-hydrogel for promoting wound healing.
(2) Formation of porous structure: Freeze-drying technology can be used to generate hydrogels with porous structures, which helps to improve the biocompatibility of hydrogels and cell growth and nutrient transport in tissue engineering applications. During the preparation process, the polymer solution is cross-linked to form a hydrogel, and then freeze-dried to obtain a porous and dry scaffold.
In summary, freeze-drying technology plays an important role in the processing and application of hydrogel materials, by maintaining the original structure and properties of the material, increasing water absorption, and enhancing stability.

